Why a Strong Government Cover Letter Matters
In the competitive world of government jobs, a well-crafted cover letter is your first impression. It’s a crucial document that complements your resume and provides an opportunity to showcase your personality, skills, and enthusiasm for the position. Unlike private sector applications, government positions often require a detailed explanation of how your qualifications meet the specific requirements outlined in the job posting. A strong cover letter is not just a formality; it’s a strategic tool to capture the attention of hiring managers and demonstrate your suitability for the role. It provides context to your resume, allowing you to elaborate on your achievements and explain how your experience aligns with the agency’s mission and values. Many candidates make the mistake of underestimating the importance of a well-written cover letter, which can significantly impact your chances of getting an interview.
Highlighting Relevant Skills and Experience
One of the primary goals of your cover letter is to highlight the skills and experience that are most relevant to the government position you’re applying for. Begin by carefully reviewing the job description, identifying the key qualifications, skills, and responsibilities. Then, use your cover letter to explicitly demonstrate how your past experiences align with these requirements. Provide specific examples of your accomplishments, using the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) to illustrate your impact. Quantify your achievements whenever possible; for example, instead of saying ‘Managed a team,’ you could write ‘Managed a team of 10 employees, resulting in a 15% increase in productivity.’ This level of detail not only shows your capabilities but also helps the hiring manager quickly see the value you would bring to their agency. Tailor each cover letter to the specific job, avoiding generic descriptions and focusing on what makes you a perfect fit.
Researching the Government Agency

Before you start writing your cover letter, it is essential to research the government agency or department. Understanding the agency’s mission, values, and recent initiatives can help you tailor your letter to resonate with the hiring manager. Visit the agency’s website, read press releases, and explore any available annual reports. This research will give you insights into the agency’s priorities and the specific skills and experience they are likely seeking. Incorporate this knowledge into your cover letter by mentioning how your qualifications align with the agency’s goals. For instance, if the agency emphasizes innovation, highlight any experience you have in developing creative solutions or implementing new strategies. By demonstrating your understanding of the agency, you show that you are genuinely interested in the position and have taken the time to prepare a compelling application. This approach is especially crucial in government jobs, where alignment with the agency’s values is highly valued.
Adapting Your Cover Letter to Each Position
It is a big mistake to use a generic cover letter for every government job application. Each position has unique requirements and the same approach will not work for all positions. Spend the time to customize your cover letter to match the specific job description and the needs of the agency. This means more than just changing the job title; it involves adjusting the content to emphasize the most relevant skills, experiences, and achievements. Use keywords and phrases from the job posting to demonstrate that you understand what the hiring manager is looking for. Avoid reusing entire paragraphs and sentences from previous cover letters. Instead, rewrite and refine your content to make it as impactful as possible for each application. This tailored approach will not only make your cover letter stand out but also increase your chances of getting an interview. If there are multiple positions at the same agency you’re applying for, you may still need to make adjustments to address the specific requirements of each individual job.
Structuring Your Government Cover Letter
Header and Contact Information

Start your cover letter with a professional header that includes your full name, address, phone number, and email address. This information should be clearly visible at the top of the page. Below your contact information, include the date and the hiring manager’s name (if you know it), title, and the agency’s address. If you cannot find the hiring manager’s name, use the title of the person responsible for hiring or ‘Hiring Manager.’ Make sure all the contact details are accurate, as this is how the agency will reach you. The header also sets the tone for the entire letter, so make sure it looks clean and professional. Avoid using unusual fonts or graphics; stick to a standard font like Times New Roman or Arial for readability.
Opening Paragraph
The opening paragraph is your opportunity to grab the hiring manager’s attention. State the position you are applying for and where you found the job posting. Clearly express your enthusiasm for the role and briefly highlight why you are a good fit. Avoid generic openings, such as ‘I am writing to express my interest…’ Instead, try to make a strong first impression by stating your key qualifications or a relevant achievement. For example, you could mention a specific skill or accomplishment that aligns with the job requirements. Also, try to personalize the opening if possible, especially if you have a connection to the agency or the specific department. The goal is to create an immediate sense of interest and encourage the reader to continue reading the rest of your cover letter. Make it clear you understand the role and are excited about the opportunity.
Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs are where you provide details about your skills, experience, and achievements. Structure these paragraphs logically, focusing on the most relevant qualifications. Use the job description as your guide, and address each key requirement with specific examples. Use the STAR method to describe your accomplishments in detail: Situation, Task, Action, and Result. Quantify your achievements whenever possible to demonstrate your impact. For instance, if you improved efficiency in a previous role, state the percentage or amount of time saved. Be concise and to the point; avoid including irrelevant information. Each paragraph should have a clear purpose, and the information should flow naturally from one point to the next. Use strong action verbs to start your sentences and to make your points more impactful. Use bullet points or subheadings to make the content easier to read and understand.
Closing Paragraph

In your closing paragraph, reiterate your interest in the position and thank the hiring manager for their time and consideration. Clearly state that you are available for an interview and provide your contact information again. Avoid phrases like ‘If you have any questions, please contact me.’ Instead, be proactive and express your willingness to discuss your qualifications further. You can also briefly mention your expectations for the next steps in the hiring process. Keep the tone professional and confident, demonstrating that you are eager to move forward in the application process. End the letter with a formal closing, such as ‘Sincerely’ or ‘Respectfully,’ followed by your full name and signature.
Formatting Your Government Cover Letter
Choosing the Right Font and Size
The format of your cover letter is just as important as the content. Select a professional font that is easy to read, such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri. The font size should be between 11 and 12 points to ensure readability. Avoid using decorative fonts or those that are difficult to read. Maintain consistent formatting throughout the document. Use clear headings and subheadings to break up the text and make it easier for the hiring manager to navigate. Pay attention to the spacing; use single spacing within paragraphs and double spacing between paragraphs. Align your text to the left for a clean look and avoid justifying the text, as this can create uneven spacing. Make sure your margins are set to 1 inch on all sides.
Using Proper Grammar and Spelling

Correct grammar and spelling are critical. Proofread your cover letter meticulously for any errors. Even small mistakes can create a negative impression and undermine your credibility. Use a grammar and spell checker, but do not rely solely on these tools; always read your letter carefully. Check for correct punctuation, subject-verb agreement, and proper use of tenses. Ensure that your sentences are clear and concise. Avoid using slang, jargon, or overly informal language. Make sure you use the correct titles, such as ‘Mr.’ or ‘Ms.,’ and that all the names of the individuals and agencies are spelled correctly. Consider having someone else review your cover letter to catch any errors you might have missed. Attention to detail demonstrates professionalism and respect for the hiring manager.
Proofreading Your Cover Letter
Proofreading is the final step in writing a winning cover letter. Even if you have used grammar and spell check, always proofread the document yourself. It is best to read the letter multiple times, each time focusing on a different aspect. First, read the letter for content and make sure it flows logically and that the information is accurate. Then, read it again slowly, looking for any grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, or punctuation errors. Consider reading the letter aloud; this can help you catch awkward phrasing or sentences that don’t make sense. Give yourself some time between writing and proofreading to gain a fresh perspective. Also, have a friend, family member, or career counselor review your letter for clarity and accuracy. A second pair of eyes can often catch errors that you might miss.
Keywords and Phrases to Include
Action Verbs for Government Cover Letters
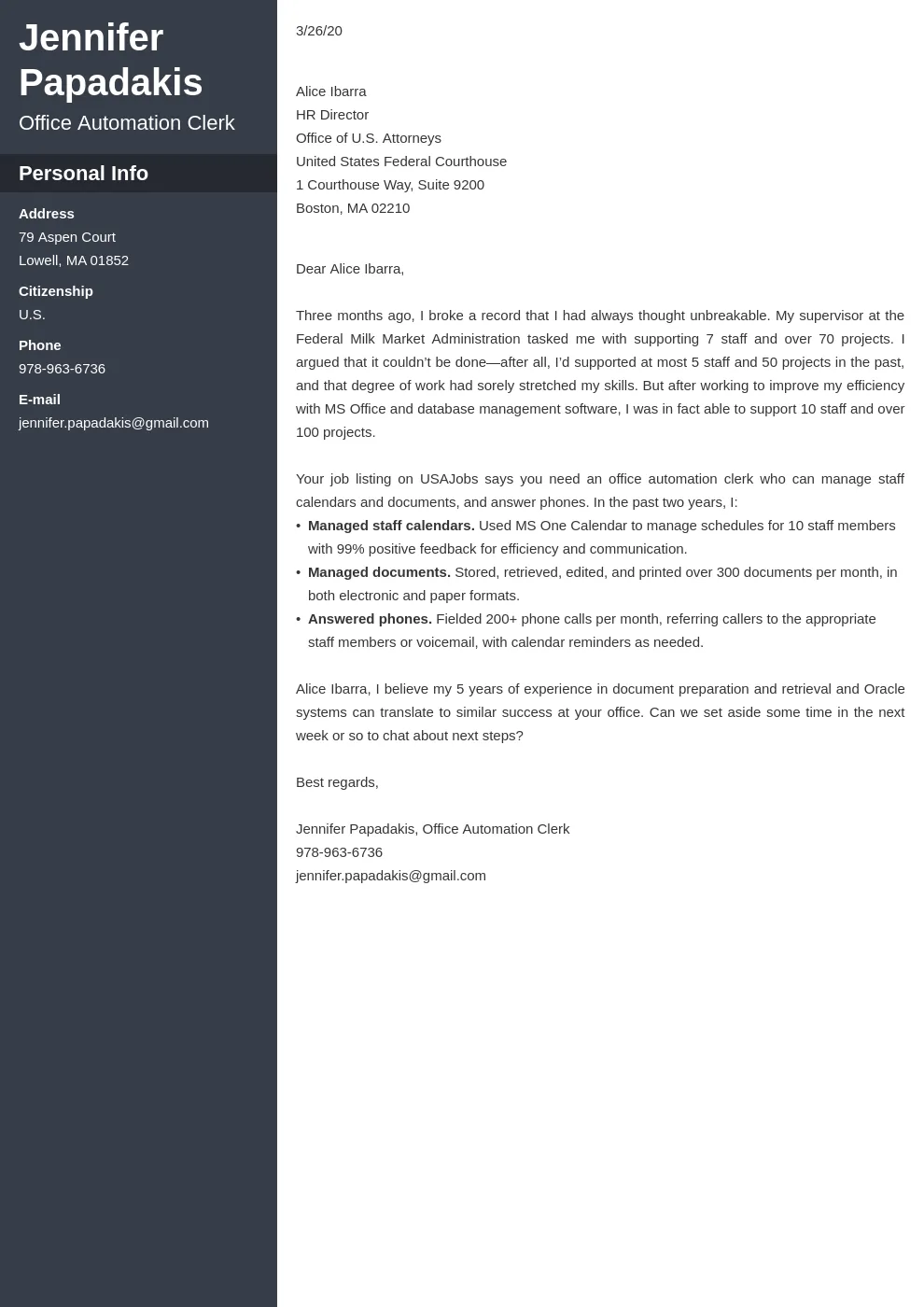
Using strong action verbs is essential in your government cover letter. Action verbs make your accomplishments sound more impactful and demonstrate your proactive approach. When describing your experiences, start your sentences with powerful verbs that convey your ability to take initiative, manage projects, and achieve results. Examples of effective action verbs include ‘Managed,’ ‘Led,’ ‘Developed,’ ‘Implemented,’ ‘Coordinated,’ ‘Achieved,’ ‘Improved,’ ‘Created,’ ‘Resolved,’ and ‘Analyzed.’ Avoid vague verbs that do not provide specific details about your achievements. Regularly review the job description and integrate the action verbs that best align with the requirements. By using action verbs, you can make your cover letter more dynamic and engaging, and effectively highlight your value to the hiring manager. Action verbs show the hiring manager what you accomplished, and show them what you are capable of doing.
Tailoring Your Letter to the Job Description
Carefully tailor your cover letter to match the specific requirements and keywords mentioned in the job description. Review the job posting thoroughly and identify the essential qualifications, skills, and responsibilities. Use the exact terminology and phrases from the job description to show that you understand the requirements and are a good match for the position. Don’t just list your skills; provide specific examples of how you have used those skills in previous roles. Highlight your accomplishments and results using quantifiable data whenever possible. For example, instead of stating ‘Managed projects,’ you could write ‘Managed three projects, resulting in a 20% reduction in project costs.’ By tailoring your cover letter, you increase your chances of getting an interview and demonstrating that you possess the qualifications the hiring manager is looking for. By using the correct keywords, you can often pass through automated screening systems used by many government agencies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Generic Cover Letters

One of the most common mistakes in cover letter writing is sending a generic letter that could apply to any job. Hiring managers quickly recognize generic cover letters and often discard them. Instead of simply restating your resume, write a cover letter that is unique to each position. Show genuine enthusiasm for the specific role and the agency’s mission. Customize your letter by highlighting the most relevant skills and experiences. Provide specific examples of your achievements and how they align with the job requirements. If possible, mention how your skills align with the agency’s priorities. Avoid using canned phrases or generic statements. Instead, write in your own voice and focus on what makes you stand out. Tailoring your cover letter demonstrates that you have taken the time to understand the position and the agency, making you a more appealing candidate.
Ignoring the Job Requirements
Another major mistake is failing to address the specific requirements outlined in the job description. Hiring managers look for candidates who can directly demonstrate how their skills and experiences match the required qualifications. Before writing your cover letter, thoroughly analyze the job description, noting the essential and preferred qualifications. Make sure your letter specifically addresses each of these requirements. Provide clear examples of how you have successfully performed the tasks and responsibilities listed in the job posting. Do not assume the hiring manager will make the connections between your experience and the job requirements. Explicitly connect your skills and accomplishments to the needs of the position. By directly addressing the job requirements, you demonstrate that you are a good fit and have taken the time to understand the position. This also shows your attention to detail, which is valuable in government positions.
Not Proofreading Your Letter
Failing to proofread your cover letter is a serious error. Errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation can create a negative impression and undermine your credibility. Hiring managers in government positions value attention to detail. Therefore, even minor mistakes can signal a lack of professionalism. Before submitting your application, carefully proofread your cover letter multiple times. Use grammar and spell check, but don’t rely on these tools alone. Read the letter slowly and carefully, looking for any errors. Consider reading it aloud to catch awkward phrasing or sentences that don’t make sense. Ask a friend, family member, or career counselor to review your letter for you. A fresh pair of eyes can often catch mistakes that you might miss. Always proofread the final version of your letter before sending it.
Government Cover Letter Examples

Reviewing examples of successful government cover letters can provide you with valuable insights. Look for cover letters that are tailored to specific positions and agencies. Pay attention to the structure, language, and formatting used. Notice how the applicants highlight their skills and experiences while addressing the requirements of the job description. Pay attention to how they express enthusiasm and clearly state their intentions. You can often find examples of cover letters online, on career websites, or in career guidebooks. However, adapt any examples to your own experience and the specific job you’re applying for. Do not copy examples; instead, use them as inspiration. By analyzing successful examples, you can improve your understanding of the qualities that make a cover letter compelling. Ensure that any example you use is specific to government jobs, as the requirements and expectations are different.
